Trigonometric Ratios In Right Triangles Answer | These ratios are given by the following trigonometric functions of the known angle a, where a, b and c refer to the lengths of the sides in the accompanying figure: The trigonometric ratios for some specific angles such as 0 °, 30 °, 45 °, 60 ° and 90° are given below, which are. Solving for a side in right triangles with trigonometry. The three major trigonometric ratios will finally relate of in one equation for triangles. What is the tangent ratio?
Every right triangle contains two angles. Solve for a side in right triangles. The standard angles for these trigonometric ratios are 0 °, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90°. This means that the ratios are independent of lengths of sides of the triangle. Cosine function (cos), defined as the ratio of the.

Solving for a side in right triangles with trigonometry. Relationship exists between the hypotenuse and the legs of right triangles and that this relationship is true for all right triangles. *****show sketchpad animation ***** identify pythagorean theorem a2 b2 c2. It is a special triangle in which one angle is 90° and the other two are less than 90°. These ratios are given by the following trigonometric functions of the known angle a, where a, b and c refer to the lengths of the sides in the accompanying figure: This means that the ratios are independent of lengths of sides of the triangle. Every right triangle contains two angles. These angles can also be represented in the form of radians such as 0, π/6, π/4, π/3, and π/2. Sine function (sin), defined as the ratio of the side opposite the angle to the hypotenuse. They are hypotenuse, perpendicular and base. From each acute angle, you can label the sides as the hypotenuse, opposite, and adjacent. Trigonometric ratios are sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant and cosecant. This is the currently selected item.
This is the currently selected item. So, all the ratios for any of the acute angles (either ∠a or ∠c) will be the same for every right triangle. These ratios of the sides do not depend on the particular right triangle. It is a special triangle in which one angle is 90° and the other two are less than 90°. What is the tangent ratio?

The three major trigonometric ratios will finally relate of in one equation for triangles. Find the three basic trigonometric ratios in a right triangle pgs: The trigonometric functions for acute angles can be defined as ratios of the sides of a right triangle. Trigonometric ratios apply to a right angle triangle only. Solving for a side in right triangles with trigonometry. Thus, it has become known as the pythagorean theorem. *****show sketchpad animation ***** identify pythagorean theorem a2 b2 c2. Sine function (sin), defined as the ratio of the side opposite the angle to the hypotenuse. What is the tangent ratio? Relationship exists between the hypotenuse and the legs of right triangles and that this relationship is true for all right triangles. Cosine function (cos), defined as the ratio of the. The trigonometric ratios for some specific angles such as 0 °, 30 °, 45 °, 60 ° and 90° are given below, which are. For a given angle, a right triangle may be constructed with this angle, and the sides labeled opposite, adjacent and hypotenuse with reference to this angle according to the definitions above.
Sine function (sin), defined as the ratio of the side opposite the angle to the hypotenuse. These ratios of the sides do not depend on the particular right triangle. From each acute angle, you can label the sides as the hypotenuse, opposite, and adjacent. This is the currently selected item. Every right triangle contains two angles.
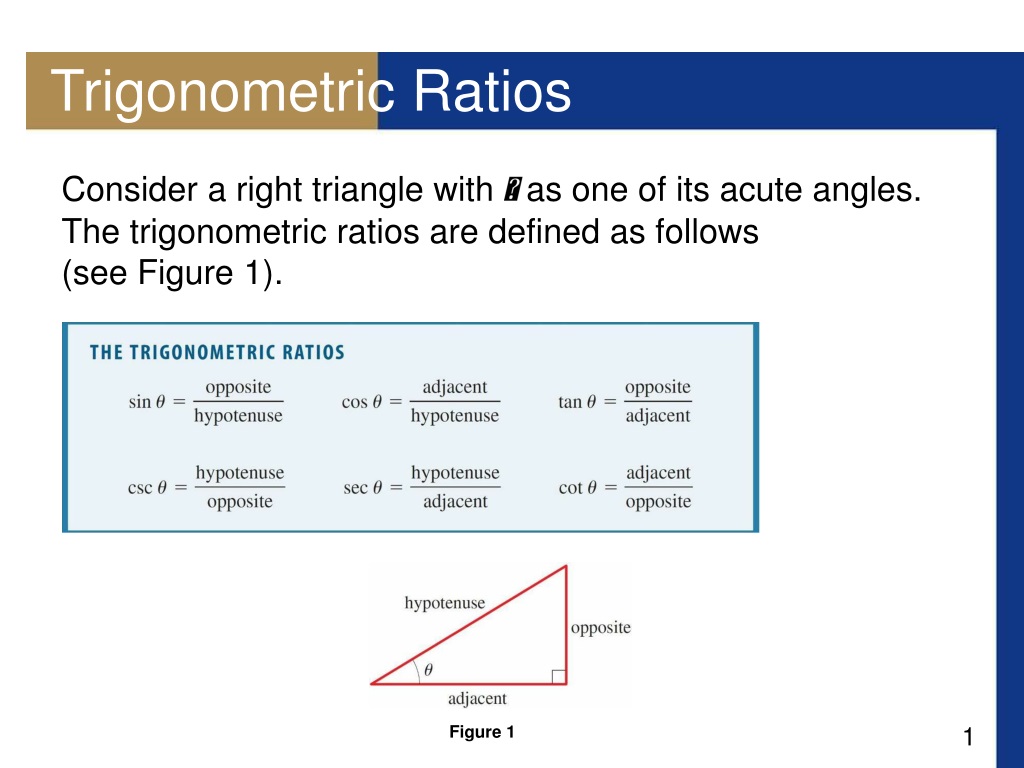
This means that the ratios are independent of lengths of sides of the triangle. What is the tangent ratio? Trigonometric ratios are the ratios between edges of a right triangle. Solving for an angle in a right triangle using the trigonometric ratios. The trigonometric functions for acute angles can be defined as ratios of the sides of a right triangle. Cosine function (cos), defined as the ratio of the. It is a special triangle in which one angle is 90° and the other two are less than 90°. Relationship exists between the hypotenuse and the legs of right triangles and that this relationship is true for all right triangles. The trigonometric ratios for some specific angles such as 0 °, 30 °, 45 °, 60 ° and 90° are given below, which are. This is the currently selected item. For a given angle, a right triangle may be constructed with this angle, and the sides labeled opposite, adjacent and hypotenuse with reference to this angle according to the definitions above. Also, each side of the triangle has a name. So, all the ratios for any of the acute angles (either ∠a or ∠c) will be the same for every right triangle.
Trigonometric Ratios In Right Triangles Answer! Solving for an angle in a right triangle using the trigonometric ratios.
comment 0 comments
more_vert